エネルギーベースモデル
深層生成モデル5
2024-03-30
PyTorch によるハンズオン
司馬博文
8/03/2024
8/21/2024
PyTorch を用いて,エネルギーベースモデルのノイズ対照学習の実装を見る.
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
# ------------------------------
# ENERGY-BASED MODEL
# ------------------------------
class EBM(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim=2):
super(EBM, self).__init__()
# The normalizing constant logZ(θ)
self.c = nn.Parameter(torch.tensor([1.], requires_grad=True))
self.f = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(dim, 128),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
nn.Linear(128, 128),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
nn.Linear(128, 1),
)
def forward(self, x):
log_p = - self.f(x) - self.c
return log_pimport math
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('Agg')
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def value(energy, noise, x, gen):
logp_x = energy(x) # logp(x)
logq_x = noise.log_prob(x).unsqueeze(1) # logq(x)
logp_gen = energy(gen) # logp(x̃)
logq_gen = noise.log_prob(gen).unsqueeze(1) # logq(x̃)
value_data = logp_x - torch.logsumexp(torch.cat([logp_x, logq_x], dim=1), dim=1, keepdim=True) # log[p(x)/(p(x) + q(x))]
value_gen = logq_gen - torch.logsumexp(torch.cat([logp_gen, logq_gen], dim=1), dim=1, keepdim=True) # log[q(x̃)/(p(x̃) + q(x̃))]
v = value_data.mean() + value_gen.mean()
r_x = torch.sigmoid(logp_x - logq_x)
r_gen = torch.sigmoid(logq_gen - logp_gen)
acc = ((r_x > 1/2).sum() + (r_gen > 1/2).sum()).cpu().numpy() / (len(x) + len(gen))
return -v, acc
#-------------------------------------------
# DATA
#-------------------------------------------
def get_data(args):
dataset = sample_2d_data(dataset=args.dataset, n_samples=args.samples)
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=args.batch, shuffle=True)
return dataset, dataloader
def sample_2d_data(dataset='8gaussians', n_samples=50000):
z = torch.randn(n_samples, 2)
if dataset == '8gaussians':
scale = 4
sq2 = 1/math.sqrt(2)
centers = [(1,0), (-1,0), (0,1), (0,-1), (sq2,sq2), (-sq2,sq2), (sq2,-sq2), (-sq2,-sq2)]
centers = torch.tensor([(scale * x, scale * y) for x,y in centers])
return sq2 * (0.5 * z + centers[torch.randint(len(centers), size=(n_samples,))])
elif dataset == '2spirals':
n = torch.sqrt(torch.rand(n_samples // 2)) * 540 * (2 * math.pi) / 360
d1x = - torch.cos(n) * n + torch.rand(n_samples // 2) * 0.5
d1y = torch.sin(n) * n + torch.rand(n_samples // 2) * 0.5
x = torch.cat([torch.stack([ d1x, d1y], dim=1),
torch.stack([-d1x, -d1y], dim=1)], dim=0) / 3
return x + 0.1*z
elif dataset == 'checkerboard':
x1 = torch.rand(n_samples) * 4 - 2
x2_ = torch.rand(n_samples) - torch.randint(0, 2, (n_samples,), dtype=torch.float) * 2
x2 = x2_ + x1.floor() % 2
return torch.stack([x1, x2], dim=1) * 2
elif dataset == 'rings':
n_samples4 = n_samples3 = n_samples2 = n_samples // 4
n_samples1 = n_samples - n_samples4 - n_samples3 - n_samples2
# so as not to have the first point = last point, set endpoint=False in np; here shifted by one
linspace4 = torch.linspace(0, 2 * math.pi, n_samples4 + 1)[:-1]
linspace3 = torch.linspace(0, 2 * math.pi, n_samples3 + 1)[:-1]
linspace2 = torch.linspace(0, 2 * math.pi, n_samples2 + 1)[:-1]
linspace1 = torch.linspace(0, 2 * math.pi, n_samples1 + 1)[:-1]
circ4_x = torch.cos(linspace4)
circ4_y = torch.sin(linspace4)
circ3_x = torch.cos(linspace4) * 0.75
circ3_y = torch.sin(linspace3) * 0.75
circ2_x = torch.cos(linspace2) * 0.5
circ2_y = torch.sin(linspace2) * 0.5
circ1_x = torch.cos(linspace1) * 0.25
circ1_y = torch.sin(linspace1) * 0.25
x = torch.stack([torch.cat([circ4_x, circ3_x, circ2_x, circ1_x]),
torch.cat([circ4_y, circ3_y, circ2_y, circ1_y])], dim=1) * 3.0
# random sample
x = x[torch.randint(0, n_samples, size=(n_samples,))]
# Add noise
return x + torch.normal(mean=torch.zeros_like(x), std=0.08*torch.ones_like(x))
elif dataset == "pinwheel":
rng = np.random.RandomState()
radial_std = 0.3
tangential_std = 0.1
num_classes = 5
num_per_class = n_samples // 5
rate = 0.25
rads = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, num_classes, endpoint=False)
features = rng.randn(num_classes*num_per_class, 2) \
* np.array([radial_std, tangential_std])
features[:, 0] += 1.
labels = np.repeat(np.arange(num_classes), num_per_class)
angles = rads[labels] + rate * np.exp(features[:, 0])
rotations = np.stack([np.cos(angles), -np.sin(angles), np.sin(angles), np.cos(angles)])
rotations = np.reshape(rotations.T, (-1, 2, 2))
data = 2 * rng.permutation(np.einsum("ti,tij->tj", features, rotations))
return torch.as_tensor(data, dtype=torch.float32)
else:
raise RuntimeError('Invalid `dataset` to sample from.')# --------------------
# Plotting
# --------------------
@torch.no_grad()
def plot(dataset, energy, noise, epoch, device):
n_pts = 1000
range_lim = 4
# construct test points
test_grid = setup_grid(range_lim, n_pts, device)
# plot
# fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(12,4.3), subplot_kw={'aspect': 'equal'})
# plot_samples(dataset, axs[0], range_lim, n_pts)
# plot_noise(noise, axs[1], test_grid, n_pts)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(4,4), subplot_kw={'aspect': 'equal'})
plot_energy(energy, ax, test_grid, n_pts)
# format
for ax in plt.gcf().axes: format_ax(ax, range_lim)
plt.tight_layout()
# save
print('Saving image to images/....')
plt.savefig('images/epoch_{}.png'.format(epoch))
plt.close()
def setup_grid(range_lim, n_pts, device):
x = torch.linspace(-range_lim, range_lim, n_pts)
xx, yy = torch.meshgrid((x, x), indexing='ij')
zz = torch.stack((xx.flatten(), yy.flatten()), dim=1)
return xx, yy, zz.to(device)
def plot_samples(dataset, ax, range_lim, n_pts):
samples = dataset.numpy()
ax.hist2d(samples[:,0], samples[:,1], range=[[-range_lim, range_lim], [-range_lim, range_lim]], bins=n_pts, cmap=plt.cm.jet)
ax.set_title('Target samples')
def plot_energy(energy, ax, test_grid, n_pts):
xx, yy, zz = test_grid
log_prob = energy(zz)
prob = log_prob.exp().cpu()
# plot
ax.pcolormesh(xx.numpy(), yy.numpy(), prob.view(n_pts,n_pts).numpy(), cmap=plt.cm.jet)
ax.set_facecolor(plt.cm.jet(0.))
ax.set_title('Energy density')
def plot_noise(noise, ax, test_grid, n_pts):
xx, yy, zz = test_grid
log_prob = noise.log_prob(zz)
prob = log_prob.exp().cpu()
# plot
ax.pcolormesh(xx.numpy(), yy.numpy(), prob.view(n_pts,n_pts).numpy(), cmap=plt.cm.jet)
ax.set_facecolor(plt.cm.jet(0.))
ax.set_title('Noise density')
def format_ax(ax, range_lim):
ax.set_xlim(-range_lim, range_lim)
ax.set_ylim(-range_lim, range_lim)
ax.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
ax.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
ax.invert_yaxis()import argparse
import os
import torch
import torch.distributions as D
d = 'cpu'
# if torch.cuda.is_available():
# d = 'cuda'
# elif torch.backends.mps.is_available():
# d = 'mps'
device = torch.device(d)
class Args:
def __init__(self):
self.epoch = 50
self.batch = 100
self.dataset = '8gaussians'
self.samples = 10000
self.lr = 1e-3
self.b1 = 0.9
self.b2 = 0.999
self.resume = False
args = Args()
# ------------------------------
# I. MODELS
# ------------------------------
energy = EBM(dim=2).to(device)
noise = D.MultivariateNormal(torch.zeros(2).to(device), 4.*torch.eye(2).to(device))
# ------------------------------
# II. OPTIMIZERS
# ------------------------------
optim_energy = torch.optim.Adam(energy.parameters(), lr=args.lr, betas=(args.b1, args.b2))
# ------------------------------
# III. DATA LOADER
# ------------------------------
dataset, dataloader = get_data(args)
# ------------------------------
# IV. TRAINING
# ------------------------------
def main(args):
start_epoch = 0
# ----------------------------------------------------------------- #
if args.resume:
print('Resuming from checkpoint at ckpts/nce.pth.tar...')
checkpoint = torch.load('ckpts/nce.pth.tar')
energy.load_state_dict(checkpoint['energy'])
start_epoch = checkpoint['epoch'] + 1
# ----------------------------------------------------------------- #
for epoch in range(start_epoch, start_epoch + args.epoch):
for i, x in enumerate(dataloader):
x = x.to(device)
# -----------------------------
# Generate samples from noise
# -----------------------------
gen = noise.sample((args.batch,))
# -----------------------------
# Train Energy-Based Model
# -----------------------------
optim_energy.zero_grad()
loss_energy, acc = value(energy, noise, x, gen)
loss_energy.backward()
optim_energy.step()
print(
"[Epoch %d/%d] [Batch %d/%d] [Value: %f] [Accuracy:%f]"
% (epoch, start_epoch + args.epoch, i, len(dataloader), loss_energy.item(), acc)
)
# Save checkpoint
print('Saving models...')
state = {
'energy': energy.state_dict(),
'value': loss_energy,
'epoch': epoch,
}
os.makedirs('ckpts', exist_ok=True)
torch.save(state, 'ckpts/nce.pth.tar')
# visualization
plot(dataset, energy, noise, epoch, device)
if __name__ == '__main__':
print(args)
main(args)大変軽量で,cpu でも5分ほどで学習できる(そのうちほとんどは画像の保存にかかる時間である).しかし,mps では次のエラーを得る.
NotImplementedError: The operator 'aten::linalg_cholesky_ex.L' is not currently implemented for the MPS device. If you want this op to be added in priority during the prototype phase of this feature, please comment on https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/77764. As a temporary fix, you can set the environment variable `PYTORCH_ENABLE_MPS_FALLBACK=1` to use the CPU as a fallback for this op. WARNING: this will be slower than running natively on MPS.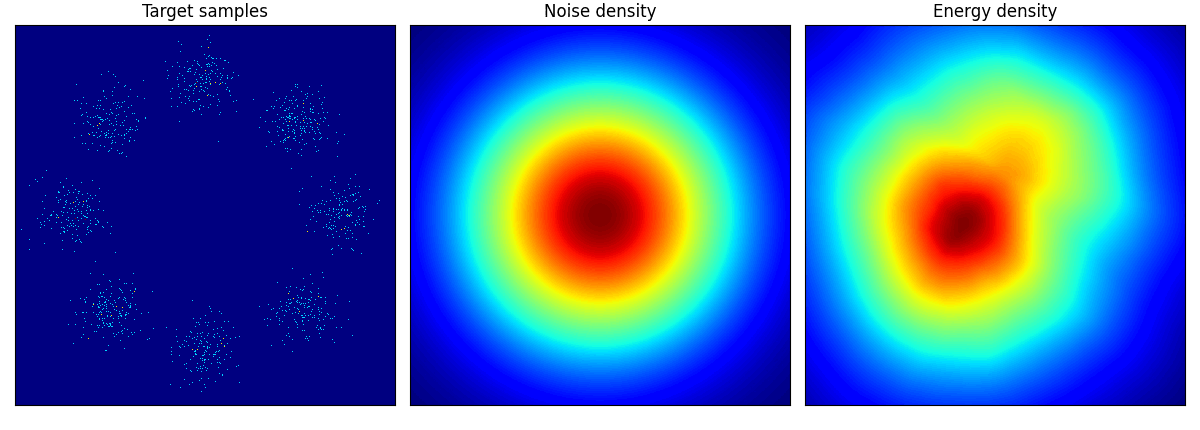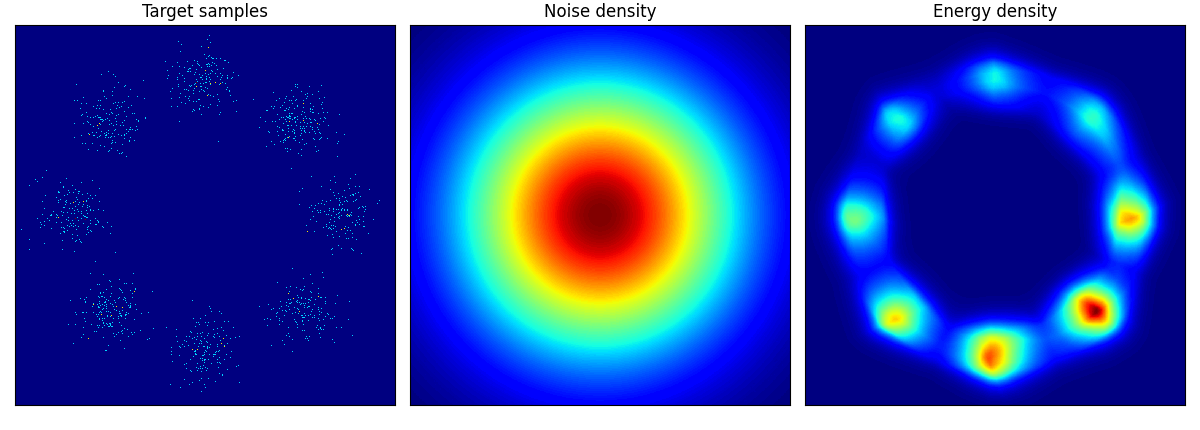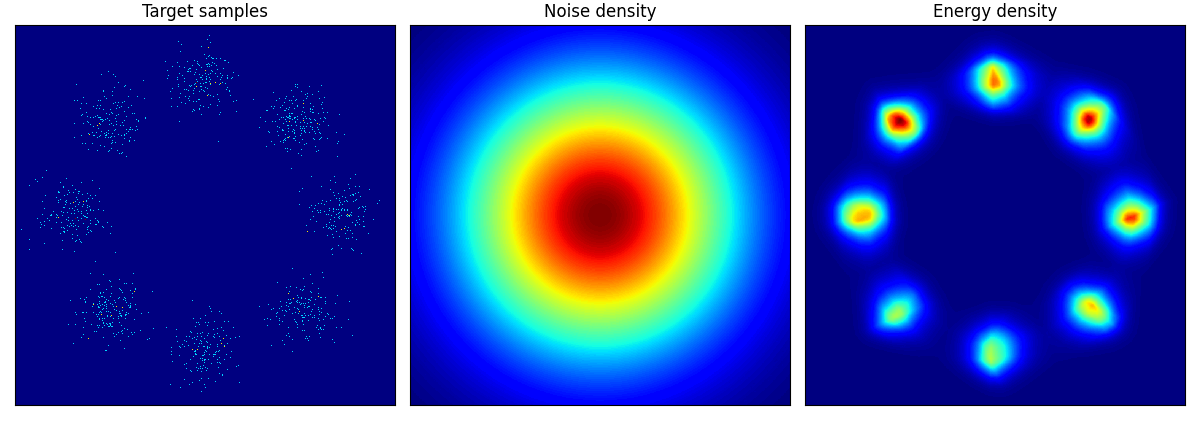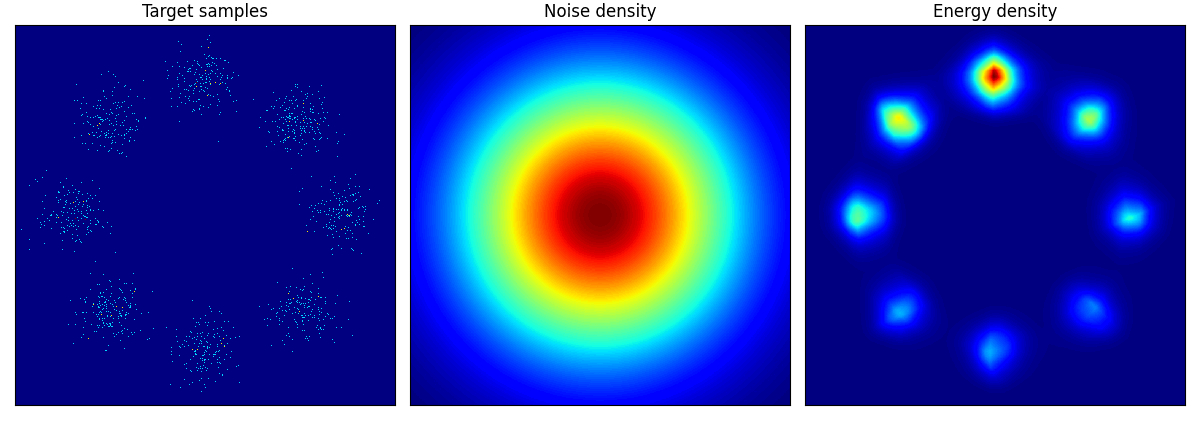
他のデータに関しても,次のように学習できる:
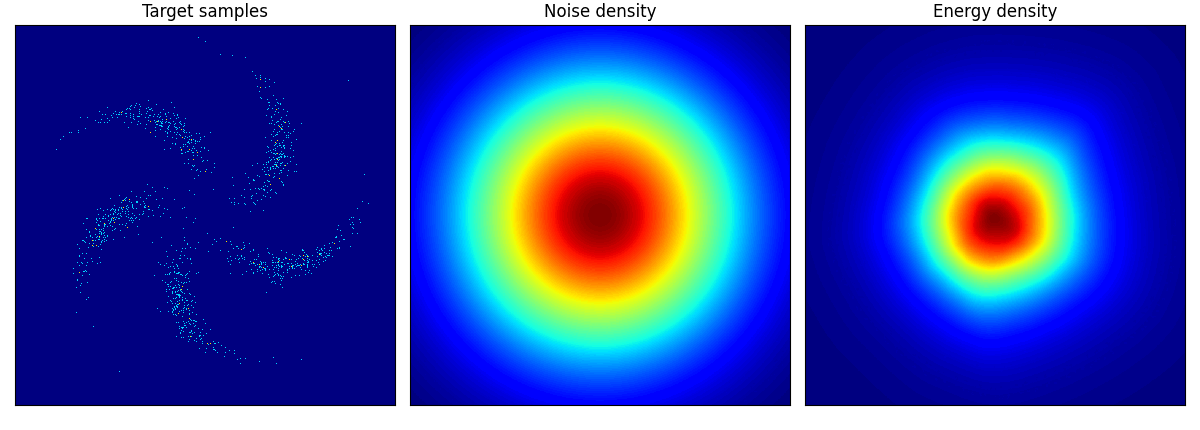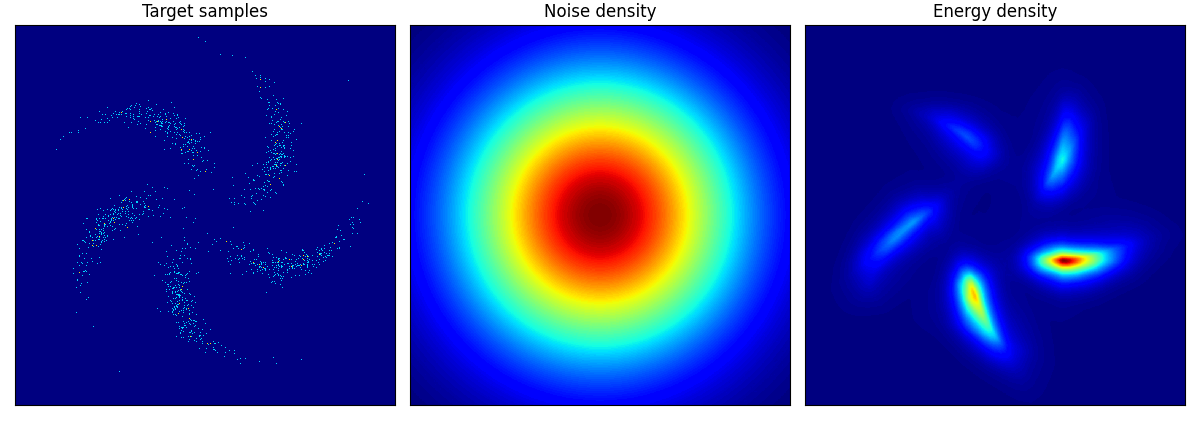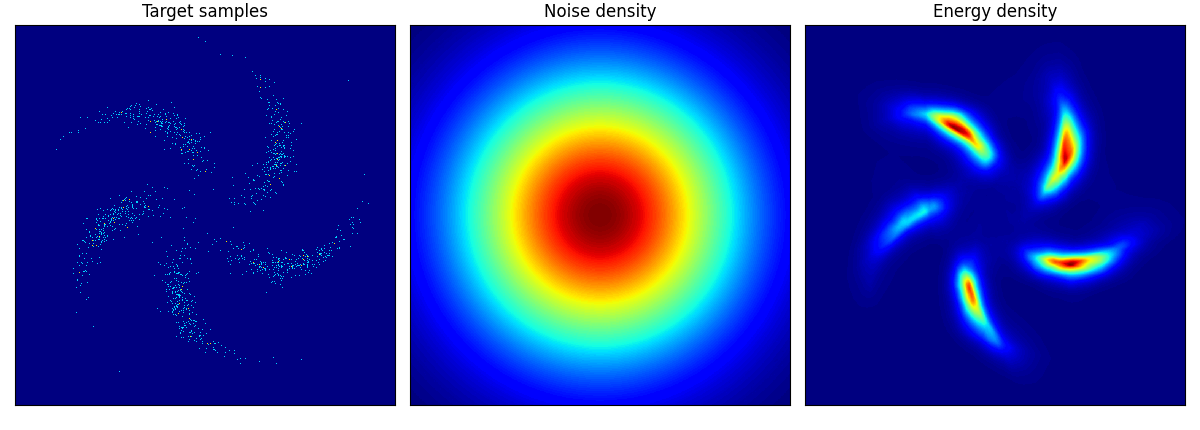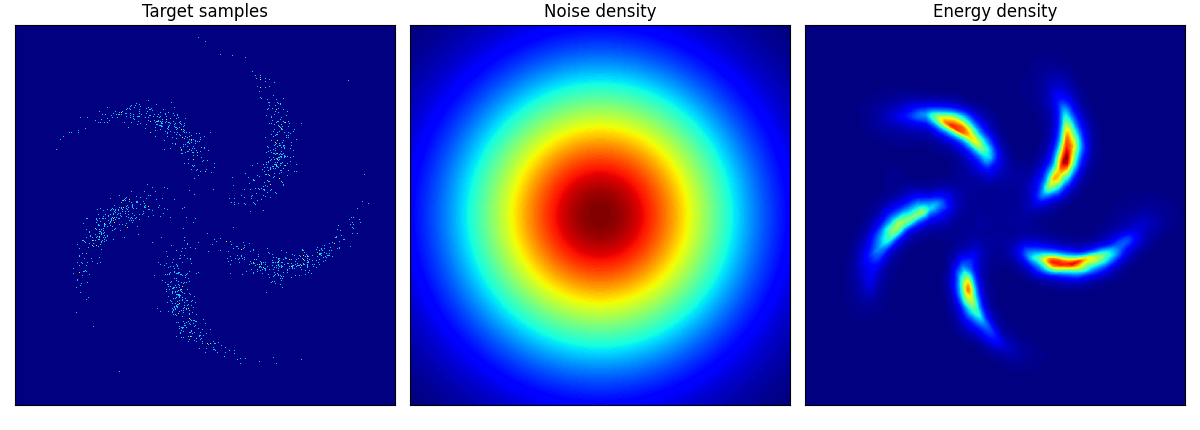
pinwheel はそれぞれの羽の尾の部分が消えてしまっているように見える.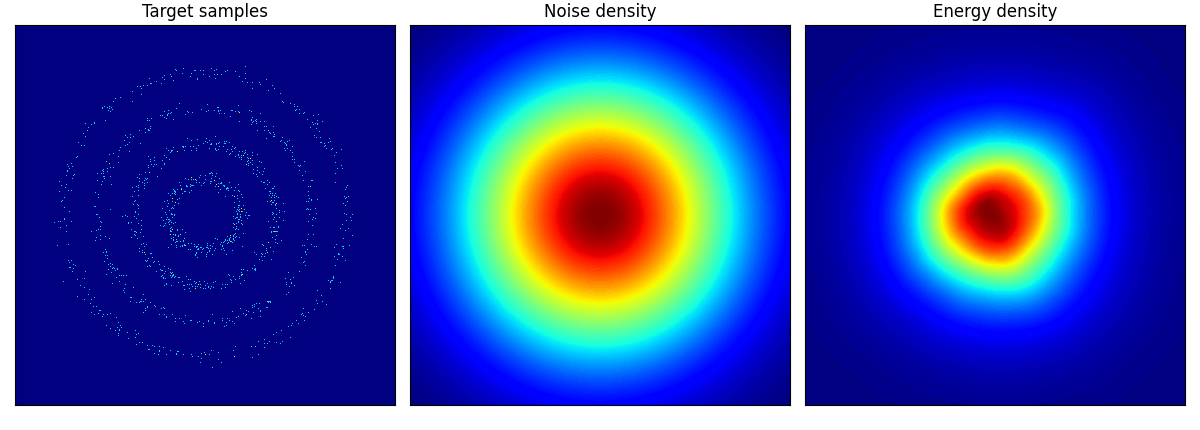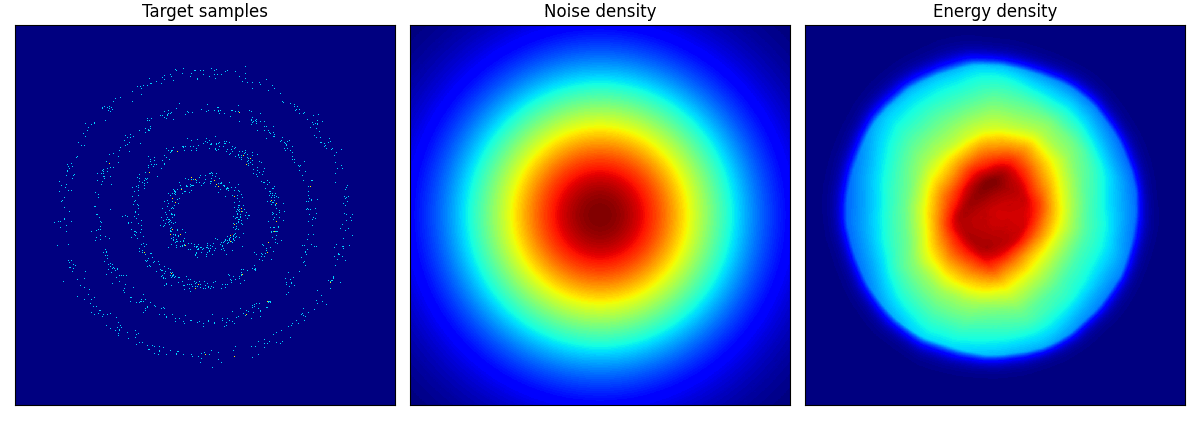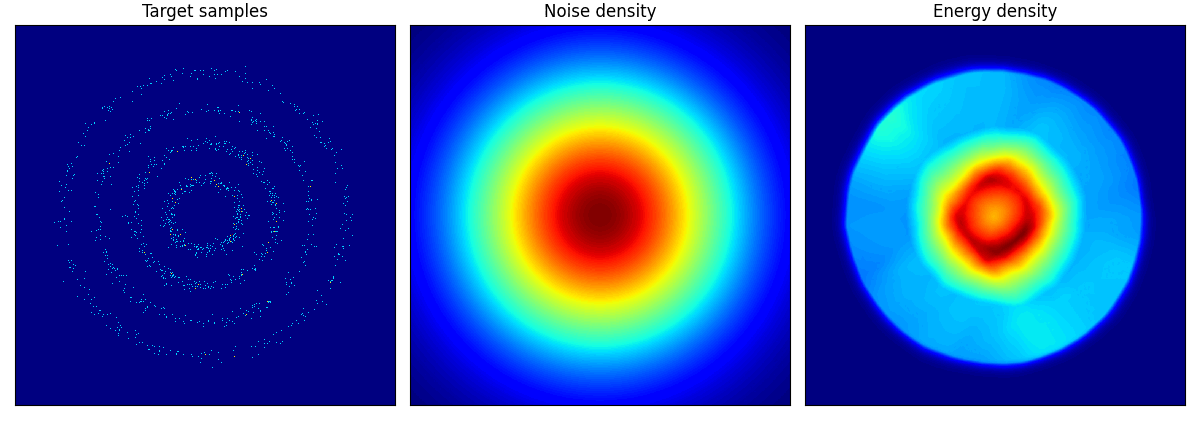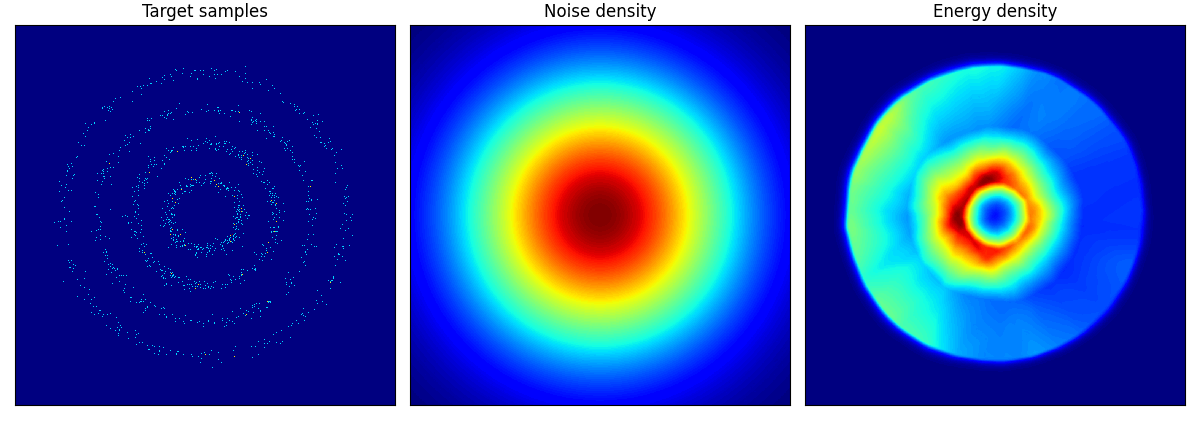
rings に関しては結構学習に苦労しているようだ.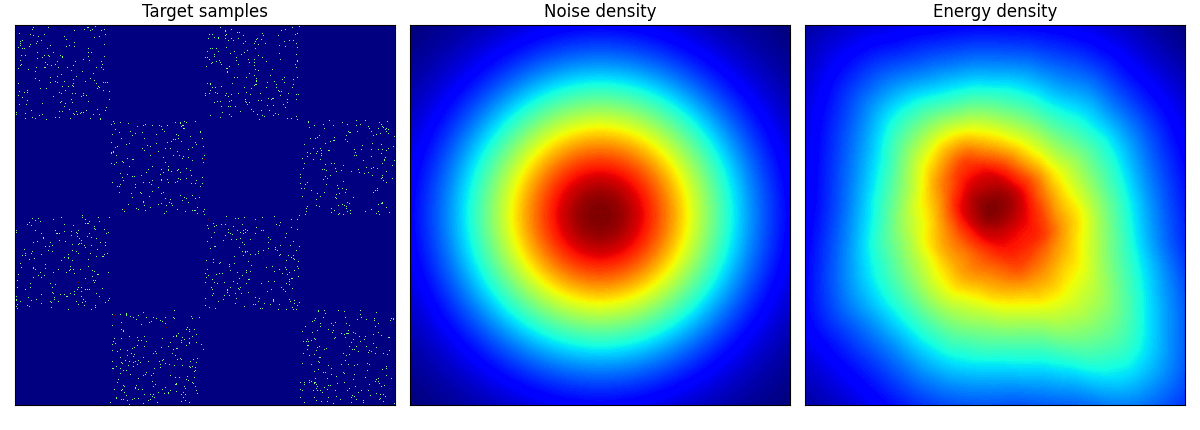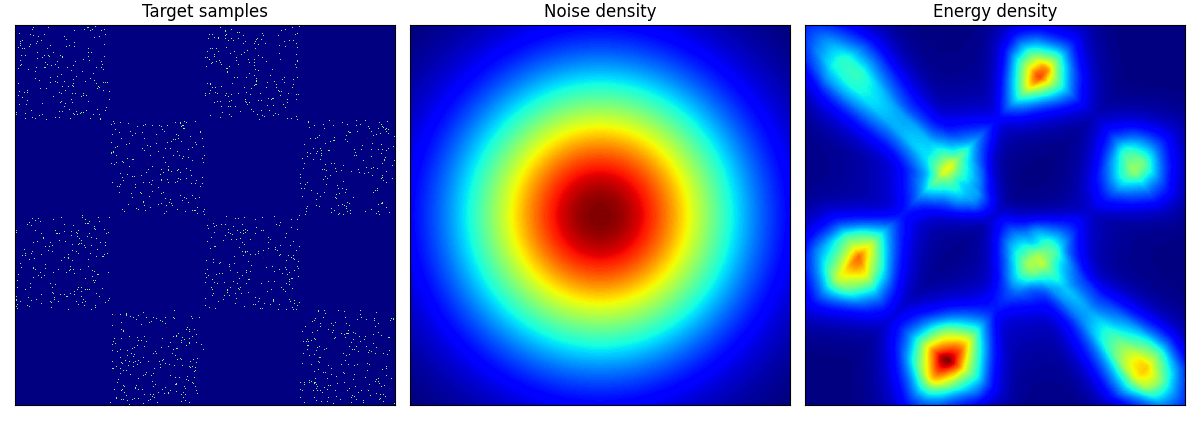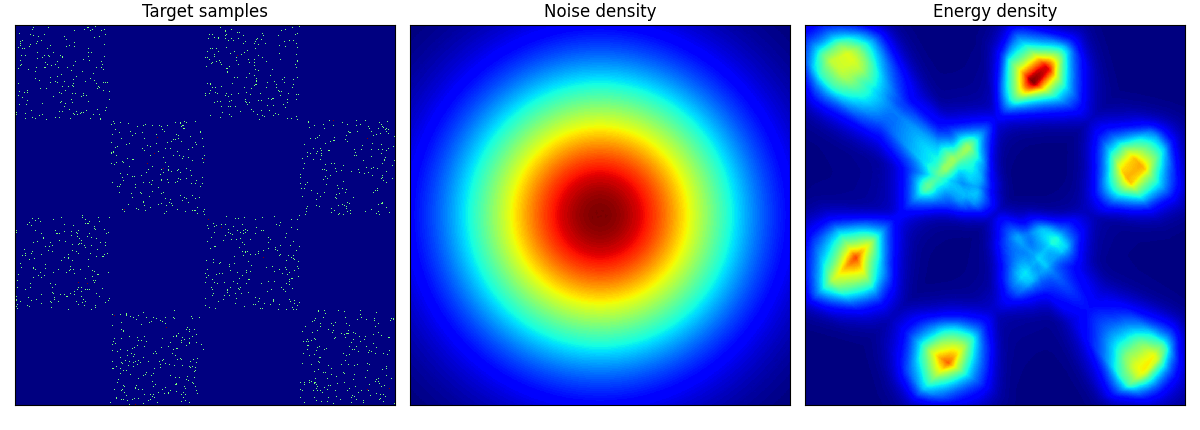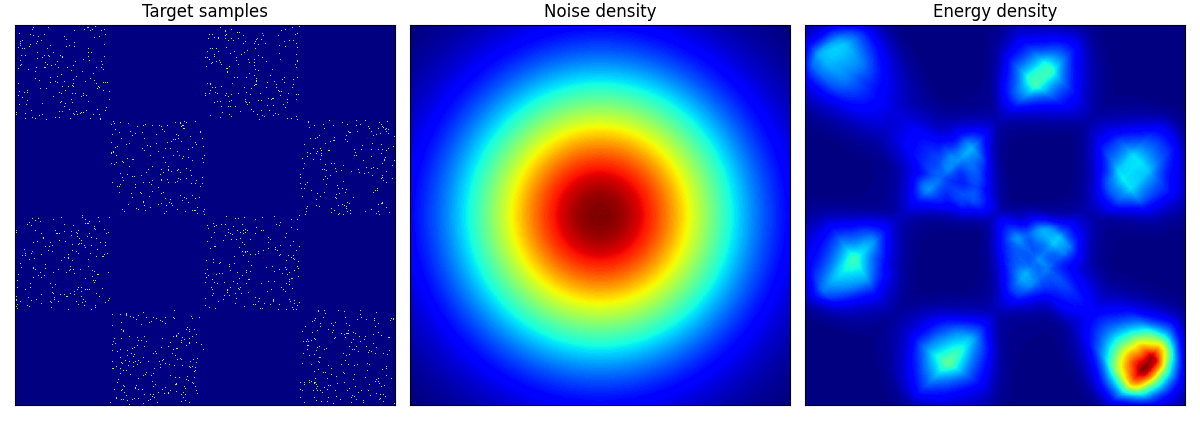
checkerboard も四角い形までは 50 epoch では再現が難しいのかもしれない.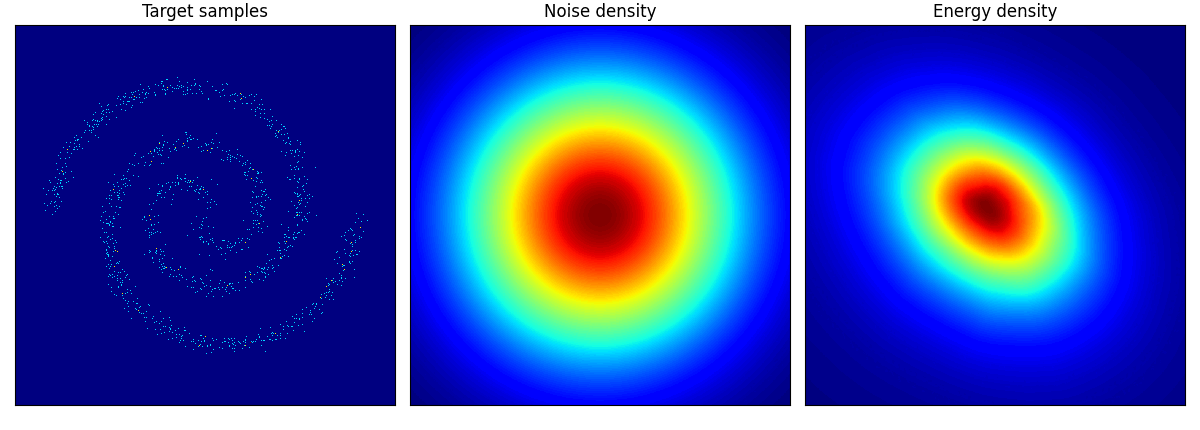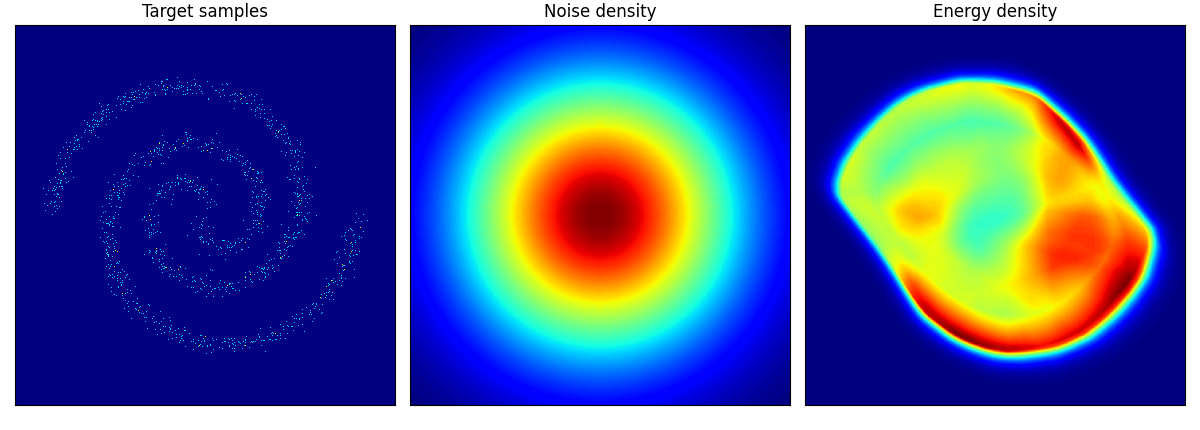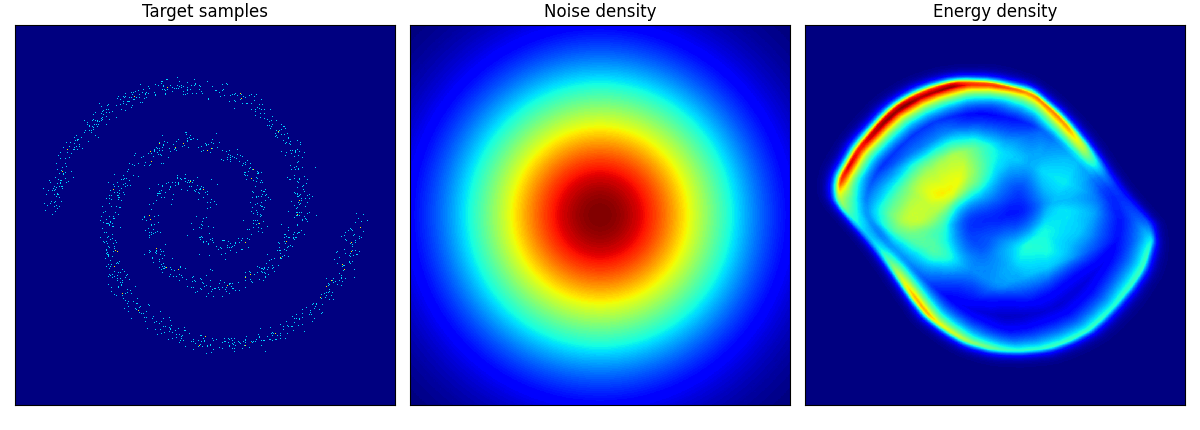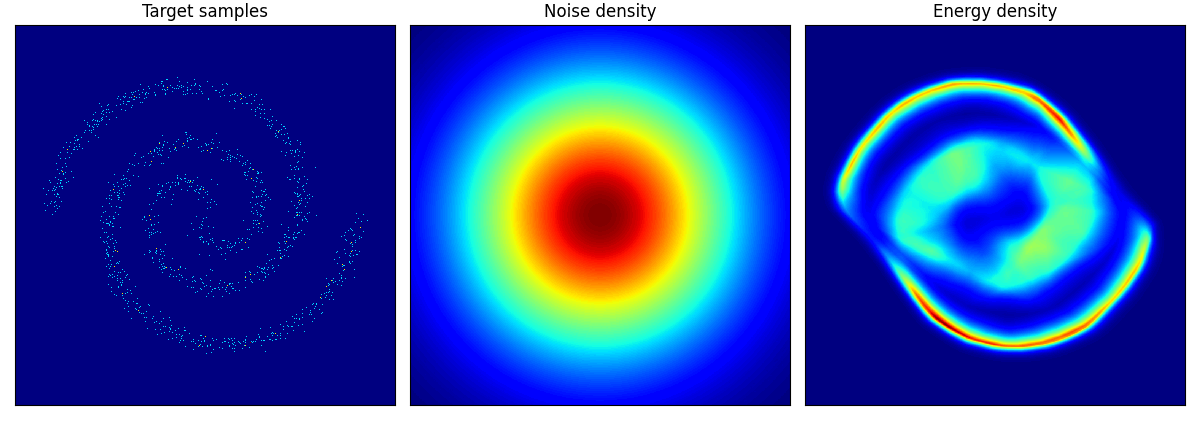
2spirals は結構トポロジーを間違えている!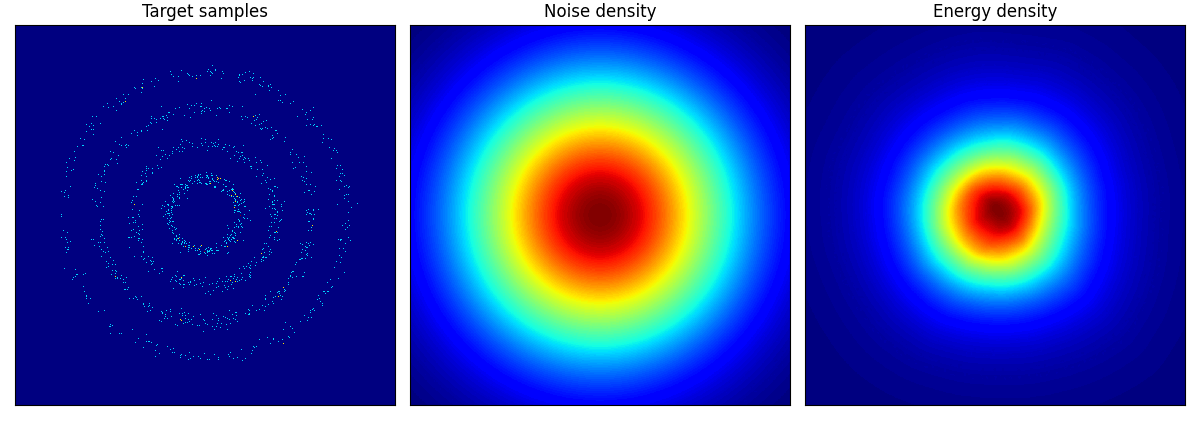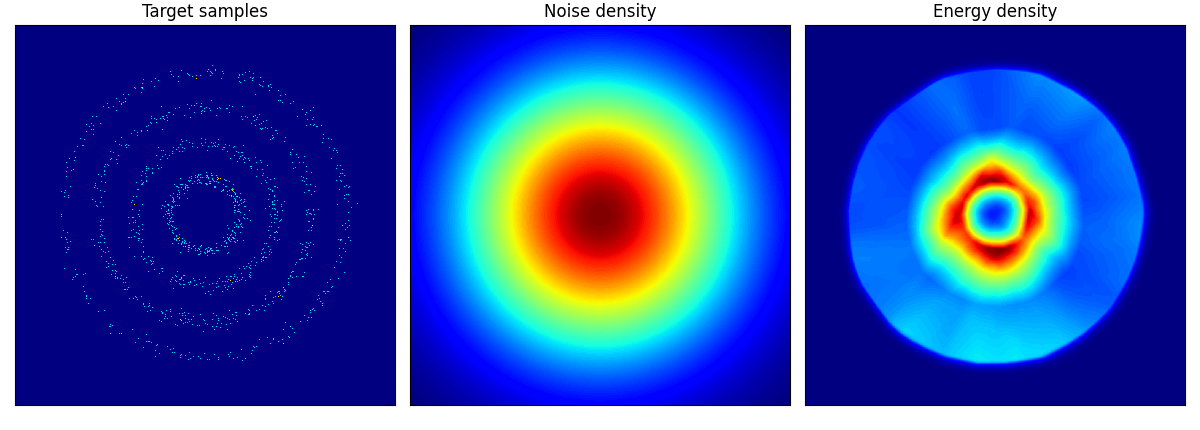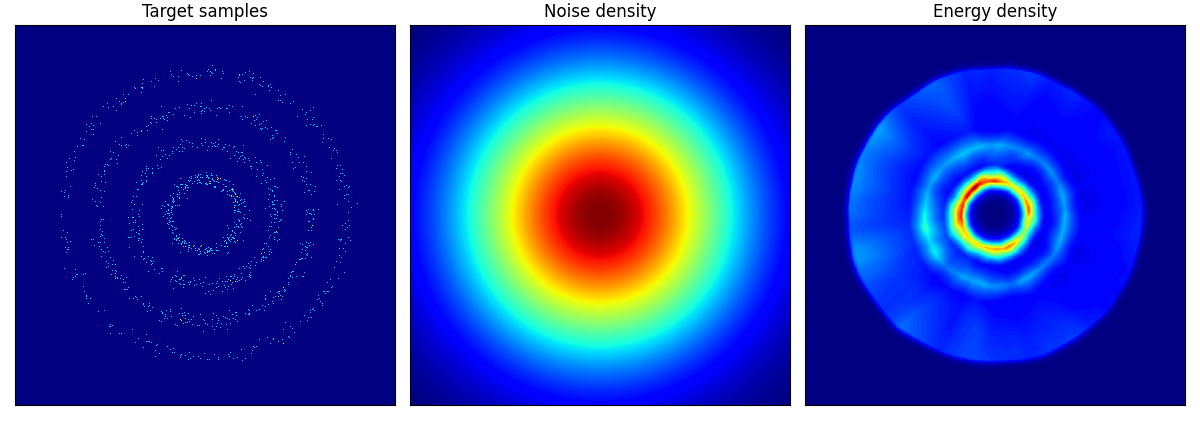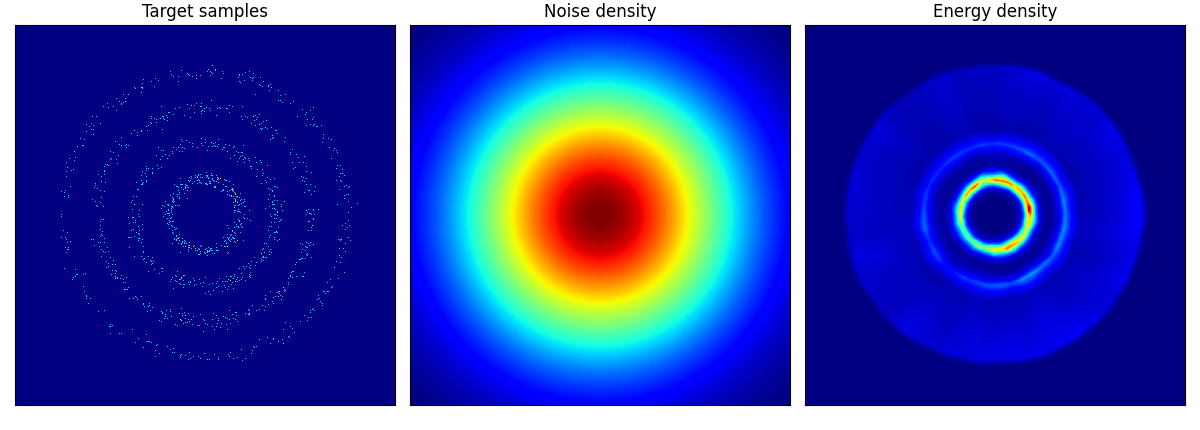
rings ロングバージョン.epoch=150 としたが,内側2輪しか再現できていない.